Elbow Specialist in Dallas and Frisco, TX
Elbow Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
Experiencing elbow pain can significantly affect quality of life because it can decrease your range of motion and prevent you from living your best life. If this sounds like you, orthopedic elbow specialists at SPORT Orthopedics + Physical Therapy want to give you a physical exam, provide you with a variety of innovative treatments, and teach you how to prevent future injuries. For more information, call a SPORT elbow pain doctor at 469-300-2832 today.
Elbow Anatomy
Because the elbow is quite the complex joint that allows you to perform countless movements, there are unfortunately many ways it can be injured. Before we go into all the different types of elbow injuries, it’s important to start with the basic anatomy of this complex joint.
For starters, the elbow is a hinge joint. This type of joint is also called a synovial joint because it’s lubricated by synovial fluid. Hinge joints only allow motion in one plane, kind of like a door. Other hinge joints in the human body include the:
- Knee
- Ankle
- Little joints in the hands and fingers
- Little joints in the feet and toes
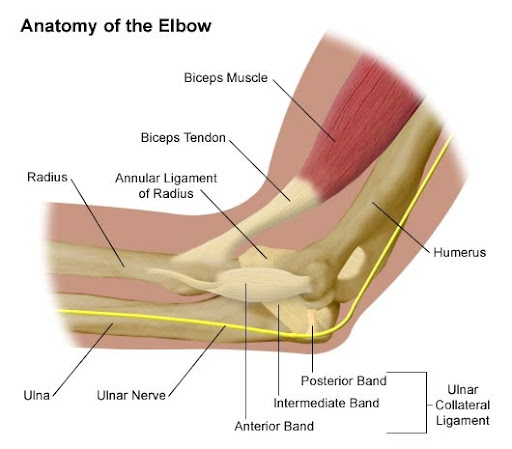
Elbow Bones and Cartilage
The elbow joint is basically created by three bones: the humerus, the ulna, and the radius. All the ends of these bones are covered in cartilage so that they can all slide against each other without causing pain. The cartilage also absorbs shock so that the bones don’t easily break.
Elbow Ligaments and Tendons
The medial collateral ligament, the lateral collateral ligament, and the annular ligament hold the elbow bones together and create the joint capsule which is filled with synovial fluid. The elbow is also made up of several ligaments which connect your muscles to your bones. The most important tendons are the:
- Biceps tendon, which connects the bicep muscle to the front of your arm
- Triceps tendon, which connects the triceps muscle to the back of your arm
Elbow Muscles
There are several muscles that surround the elbow and allow it to move properly. They include:
- Biceps Brachii: This is your bicep muscle on the front of your upper arm. It can flex as well as twist the forearm until the palm turns upward.
- Triceps Brachii: This is your tricep muscle on the back of your upper arm. It allows the arm to extend and it stabilizes the elbow.
- Brachioradialis: This is a lower arm muscle that’s on the outside of the forearm. It allows you to flex your arm at the elbow.
- Anconeus: This is a lower arm muscle that sits right at the arm crease. It allows you to extend the arm at the elbow.
- Brachialis: This muscle surrounds the bicep muscle and allows you to move the elbow towards the body.
- Pronator Teres: This muscle extends from right above the elbow joint to about the middle of your forearm. It allows you to flex the elbow and rotate your forearm until your hand faces backwards.
How Many Joints Do Humans Have?
Doctors estimate that the average human has anywhere from 250 to 350 joints.
Common Causes of Elbow Pain and Treatment Options
As you can see, numerous bones, muscles, and tendons can be involved in an elbow injury and can cause severe pain. An elbow pain doctor may diagnose you with one of the elbow problems listed below.
Fractured Elbow
Broken bones in the arm may be the cause of your elbow pain. Sports injuries, car accidents, and falls can easily cause a broken arm. Sometimes patients with a fractured elbow may wait to see an elbow doctor because they may still be able to move their arm. But if you’re in a lot of pain and your arm doesn’t look like it normally does, you may have fractured it. Oftentimes, fractured elbows require surgical treatment from an orthopedic surgeon. After surgery, patients generally have to wear an elbow brace or arm cast for several weeks during the healing process.
Dislocated Elbow
A dislocated elbow can feel almost as painful as a fractured elbow. It happens when an accident knocks one of the elbow bones out of place. A common cause of a dislocated elbow is when someone tries to catch themselves during a fall by putting their hand out. Most of the time, an orthopedic doctor will pop the elbow back into place and tell you to wear a splint or a sling to promote healing.
Elbow Sprains or Strains
Sprains and strains are elbow injuries that don’t require surgery. An elbow strain happens when muscles are stretched or torn. Meanwhile, an elbow sprain happens when ligaments are stretched or torn. One common example is a UCL tear. Sprains and strains can quickly heal with nonsurgical treatment options.
Bursitis
Almost any joint can develop bursitis, which is inflammation of the bursae. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints. Bursitis is often caused by repetitive movements, accidents, or infections. Bursitis rarely requires surgical intervention. Instead, this condition can improve with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can reduce pain, and ice therapy, which can reduce swelling.
Tennis Elbow or Golfer’s Elbow
These elbow conditions are also caused by repetitive movements which damage the surrounding tendons. Tennis elbow generally causes pain on the outside of the elbow while golfer’s elbow causes pain on the inside of the elbow. Despite the names, any kind of overuse injuries can cause golfers or tennis elbow, not just those sports. Dallas Physical therapy and stretching exercises can generally improve this type of elbow injury.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Both cubital tunnel syndrome and carpal tunnel syndrome are trapped nerve conditions. In other words, these conditions happen when nerves get pinched. This condition may require surgical intervention through a procedure called cubital tunnel release. This elbow surgery basically decompresses the ulnar nerve, which is the pinched nerve that causes elbow pain in this condition.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a type of joint inflammation where the immune system attacks healthy tissue in the joints. There are many types of arthritis, but the most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Both types can affect the elbows and cause significant elbow pain. Treatment can include orthopedic surgery, physical therapy, pain medications, and more, depending on the severity of the condition.
Osteochondritis Dissecans
This condition is more common in the knees, however, it can affect the elbows too. Osteochondritis dissecans causes bones to die and break loose due to lack of blood flow. If you’re suffering from this condition, contact an orthopedic doctor at SPORT to create a treatment plan.
At Home Treatment for Elbow Pain
You can treat elbow pain and many elbow conditions at home. The most effective at-home treatments are resting, taking pain medications, using ice packs, wearing a compression bandage on the elbow, and stretching gently every day can promote healing. If these treatments don’t improve your elbow pain within a few days, you should see an elbow pain doctor as soon as possible.

When Should I Call a Doctor for Elbow Pain?
As stated previously, you should certainly receive medical treatment if your elbow pain doesn’t improve with at-home treatments. Other signs that you need to see a doctor are:
- Intense pain, swelling, bruising, and redness
- Reduced range of motion following an accident or an injury, specifically an inability to bend your arm without pain
- Fever following an injury or accident
Call SPORT Orthopedics + Physical Therapy Today
If you’re suffering from any kind of joint, bone, or muscular injury, you need orthopedic care from the best orthopedic surgeon in Dallas. We will do everything we can to get you back to a pain free life. Call us today at 469-200-2832.


