Knee Replacement Surgery in Dallas, TX
What to Expect from Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee Joint Replacement in Dallas, TX
Knee replacement surgery, or knee arthroplasty, is a procedure commonly performed to remove and replace an arthritic or damaged joint with a prosthesis (artificial joint). It is generally reserved for situations where other treatment options have failed to provide sufficient pain relief and restore range of motion.
It is crucial to work with a surgeon with considerable experience in this area, as it requires significant skill. Luckily, when you work with SPORT, you’ll be working with the best knee surgeon in Dallas.
At SPORT Orthopedics + Physical Therapy, knee replacement is the most common type of joint replacement our orthopedic surgeons perform. The vast majority of patients who have a knee replacement do so to treat severe osteoarthritis.
However, rheumatoid arthritis and traumatic injury to the knee may also result in the need for joint replacement. Those in need of a knee surgeon who is highly skilled at performing knee replacements should contact SPORT as soon as possible.
To schedule an appointment with us, please call our office at 469-200-2832 or schedule an appointment online. If you’re recovering from knee surgery, read our blog on what not to do after knee replacement surgery for recommendations and best practices.
Anatomy of the Knee
Your knee is a hinge joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) with the shin bone (tibia). There is a smaller bone that runs beside the shin bone (fibula) and the kneecap (patella) at the front of your knee. Surrounding these bones and connecting all around them are strap-like tissues called ligaments that keep the knee steady.
They connect the bones to each other, and the tendons attach the muscles to the bones. All of these body parts must work together for the knee to have proper function. The following ligaments are crucial for the joint health of your knee.
- Our ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) keeps the shin bone from sliding forward on the thigh bone.
- Our PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) keeps the shin bone from sliding backward on the thigh bone.
- Other ligaments on either side of the knee (medial and lateral collateral ligaments) keep the bones from shifting from side to side.
Where the shinbone and thigh bone meet are two cushions made from cartilage (medial and lateral meniscus). Shaped like the letter “C,” this cartilage provides shock absorption and keeps the two bones from rubbing together.
There are also several sacs inside the joint that provide lubrication for movement. These are called bursae. If these sacs become inflamed or irritated, it can cause a painful condition called bursitis.

What Is a Knee Joint Replacement?
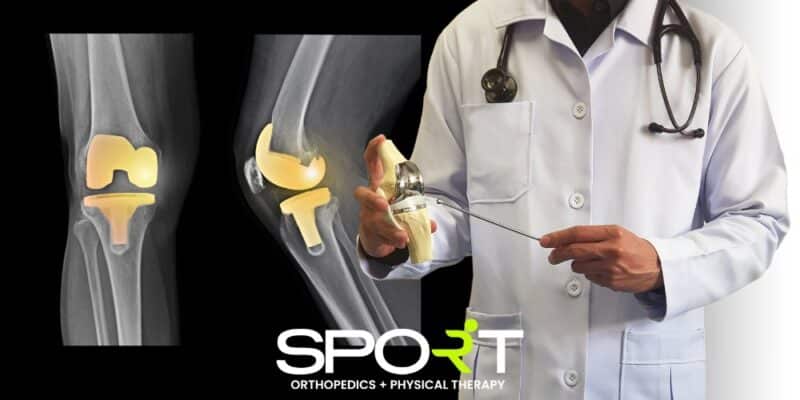
What Is a Knee Joint Replacement?
A knee joint replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves resurfacing a knee that has been damaged by injuries or knee conditions. Surgeons performing these knee surgeries will use the latest techniques and medical devices to place caps on the ends of the bones in the joint.
These caps are usually usually made of metal or polyethylene plastic. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, they may undergo either partial, total, or bilateral knee replacements.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
There are a few different types of knee joint replacement techniques that we use in sports medicine. The four major techniques for replacing knee joints are as follows.
- Partial knee replacement surgery
- Total knee replacement surgery
- Kneecap replacement surgery
- Revision knee surgery
If both of a patient’s knees require surgery, they may be able to undergo what is called a bilateral knee replacement. This procedure uses one or more of the above techniques to replace both knees at once. Although it is slightly riskier than replacing one knee at a time, certain patients are eligible.
Most patients who undergo a knee joint replacement do so when their knee joint health has significantly deteriorated. This is usually due to knee arthritis or osteoarthritis. We prefer to try non-surgical approaches first, such as knee gel injections or rehabilitation.
However, some conditions will only worsen your pain, and the disruptions to your daily life may worsen over time.
Other conditions that may warrant a knee replacement include the following.

- Gout
- Hemophilia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic knee inflammation
- Knee deformity
- Bone growths in the knee
- Significant cartilage loss
- Bone death in the knee joints
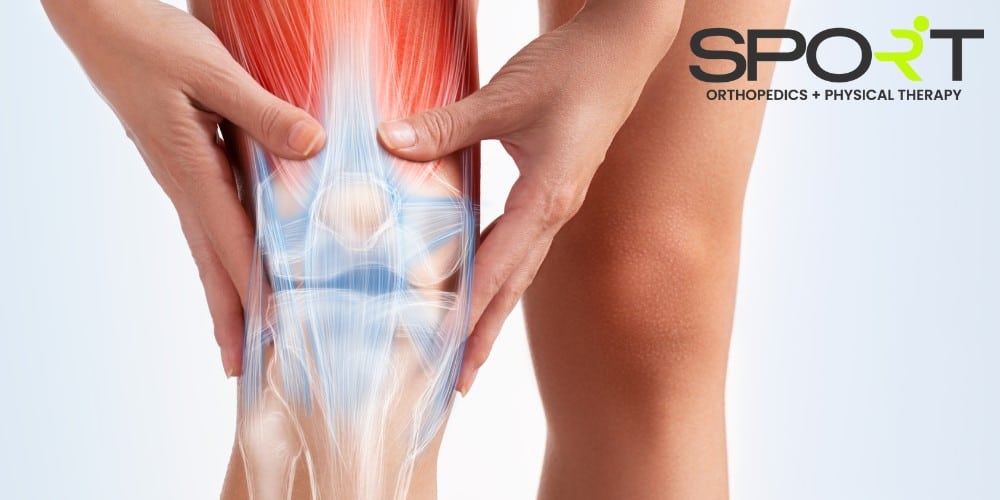
What Causes Knee Pain?
Severe knee pain can arise in people of all ages, and is a common complaint, along with hip pain. Many different conditions and injuries can cause knee pain, including infections, sports injuries, gout, ligament tears, and ruptured cartilage. The two most common reasons why someone may have knee surgery include osteoarthritis and knee injuries.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting about 21 million Americans. It tends to develop as people grow older. Osteoarthritis can result from overuse of a joint during sports or work.
The most common reason you may need a partial knee replacement is arthritis (osteoarthritis). Arthritis causes swelling and damage around the padding in the knee (cartilage), causing it to wear away.
As the bones begin to rub against one another, abnormal bone growths, called spurs, can grow around the joint. The bone spurs can cause severe pain and swelling while disrupting movement.
Osteoarthritis usually happens slowly and may take years to get bad enough for you to need a partial knee replacement.
Knee Injuries
Some patients may need a partial knee replacement years after an old injury, like a car accident or another type of old injury to the cartilage or ligaments. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are not candidates for a partial knee replacement because it is a disease of the whole joint, and this procedure just treats one area.
What Are the Treatment Options for Knee Pain?
Many orthopedic specialists prefer to try non-invasive techniques before considering surgery. If your knee can become healthy again without surgery, this is always preferable. Surgery is extremely effective, but it has more downtime and longer healing periods than non-surgical options. Therefore, we may recommend other non-invasive options before resorting to surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatment
If you are considering a partial knee replacement, you have probably tried non-surgical treatments. If you have not, your doctor will want you to start with those. He or she may suggest losing weight, adjusting your exercise routine, supportive braces, medication or physical therapy. There are injections that can be placed into the knee that can relieve pain for weeks or months, allowing you to put off the surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment will involve replacing the worn cartilage with metal or plastic replacement parts. To do the surgery, your doctor will replace the area of arthritis with a metal cap and put in a plastic liner. This will let the metal and plastic move smoothly like your old knee should have. Without the arthritis and painful tissue in your knee, you will be able to move and enjoy activities again.
Your doctor will closely examine your X-rays to determine where your arthritis is most severe and decide if you are a good candidate for a partial replacement. If you have very advanced arthritis, you will not be a good candidate for a partial replacement and will need a total knee replacement. Your doctor will help you make the right decision.
What Is the Alternative to Knee Replacement Surgery?
There are a few alternatives to a total knee replacement. Some use a combination of procedures to rebuild a knee using donor tissue and stem cells to regrow the articular cartilage.
How to Prepare for Your Knee Joint Replacement in Dallas
Your surgeon will inform you of how best to prepare for both the surgery and for your recovery period afterward. Below, we outline a few tips on how to make your recovery from knee replacement go as smoothly as possible.
Prepare your home beforehand. If you have stairs in your home, arrange everything so that you won’t need to use them. Bring your necessities downstairs and arrange a place to sleep. Keep everything you need at about hip level for easy access.
As soon as your physical therapist says you can use stairs, you can return everything to how it was. If you use a walking aid after the surgery, make sure that your home has no trip or slip hazards. If your toilets are lower to the ground, consider using a riser to make it easier to use.
Take time off for your recovery. Don’t try to go back to work right away. Take at least a few days to a week off to relearn how to walk with your new joint. While you do need to rest, you should also get up and walk around a little each day.
Refrain from driving or doing too much. Because of the movements it takes to get into and out of a car, you likely won’t be able to drive for a while. Arrange for someone to help you get around if necessary. Additionally, don’t push yourself too hard. Recovery can be tough, but that doesn’t mean you should risk damaging your new knee.
What Can I Expect from Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery aims to alleviate pain and enhance joint function. It begins with a comprehensive evaluation including medical history, physical exams, and imaging tests. Depending on the damage, either total or partial knee replacement may be recommended.
Total knee replacement is performed when all three compartments of your joint have arthritis damage. Partial knee replacement, or unicompartmental knee replacement, may be preferred if arthritis is confined to only one area of the knee joint.

The surgery, lasting one to two hours, can be done via traditional open approach or minimally invasive methods. Recovery varies; some may qualify for outpatient surgery, while others may need hospitalization for one to four days. Regardless, patients typically start walking with assistance soon after.
After the procedure, knee replacement surgery patients can expect a noticeable improvement in flexibility and far less pain within a month. However, exercising your knee is important to reduce swelling and strengthen your muscles, which is why post-operative physical therapy is critical to a successful recovery. Your full knee replacement recovery time may be anywhere from three to six weeks.
Risks and Complications of Knee Joint Replacements
Every surgery has a certain degree of risk, but knee replacements are generally safe and effective for healthy individuals. However, complications are still possible. This is especially true if patients make any of the top 5 mistakes after knee replacement. These mistakes, such as skipping physical therapy and rushing the recovery process, can lead to serious complications.
Below, we outline the potential risks associated with knee replacements.
- Infections
- Knee stiffness
- Persistent knee pain
- Failure of the implant
Knee Replacement Surgery FAQs
What's the Best Age to Have a Knee Replacement?
We typically don’t recommend knee replacement surgery if you’re younger than 50. While recommendations for surgery are based on a patient’s pain and disability, most patients who undergo a total knee replacement are over the age of 50.
What Happens if You Wait Too Long for Knee Replacement?
If your knee replacement surgery isn’t done at the appropriate time, total joint replacement can bring your function score up, but not to “normal”.
If a patient waits until he or she can’t sleep or is in so much pain that their mobility is limited, their score typically drops, and their post-knee replacement surgery score may only get up to 32. This is way below where we’d like our patients to be. If you experience symptoms such as knee instability, you may require surgery.
Will I Need Physical Therapy After a Knee Joint Replacement?
Physical therapy is extremely important for patients who have undergone a joint replacement. It will help to restore your strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the joint. It may also help you return to your everyday activities a little faster.
At SPORT, we offer on-site physical therapy. Our surgeons and physical therapists will work closely to develop a plan for your recovery. When they have arranged your physical therapy appointments, we strongly recommend going to every appointment that you can.
How Much Does a Knee Joint Replacement Cost?
This depends on a number of factors, including the severity of the damage and the complexity of the surgery. At SPORT Orthopedics + Physical Therapy, we like to maintain transparency with our pricing. That’s why we have a page dedicated to our cash pricing options. We also accept insurance, which could greatly affect your out of pocket costs for a procedure.
Best Knee Surgeon in Dallas for Knee Joint Replacements
If you suffer debilitating knee arthritis and other treatments have failed to provide relief, it may be time for a knee replacement. For the area’s leading knee replacement surgeon, contact SPORT Orthopedics + Physical Therapy today. We have four offices to serve you in Dallas, Frisco, Prosper, and Wylie.
An orthopedic surgeon in Frisco will let you know which surgical approach is best for you and explain the procedure in detail. To schedule an appointment, call (469) 200-2832 or use our convenient online form.


